Color Theory
What is color theory?
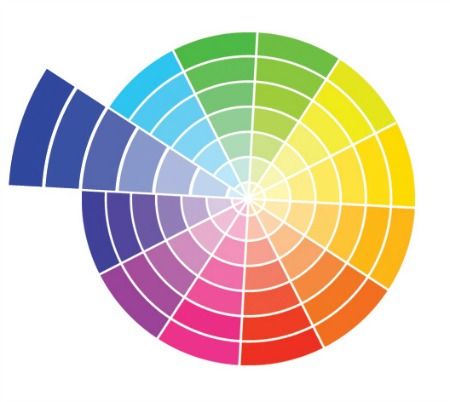
Color theory is the study of color relationships and how they affect human perception. It includes the color wheel, color harmonies, and the psychological and emotional effects of color. The color wheel is a visual representation of the relationships between colors. It is typically divided into primary, secondary, and tertiary colors. The primary colors are red, blue, and yellow. Secondary colors are created by mixing primary colors. Tertiary colors are created by mixing primary and secondary colors.
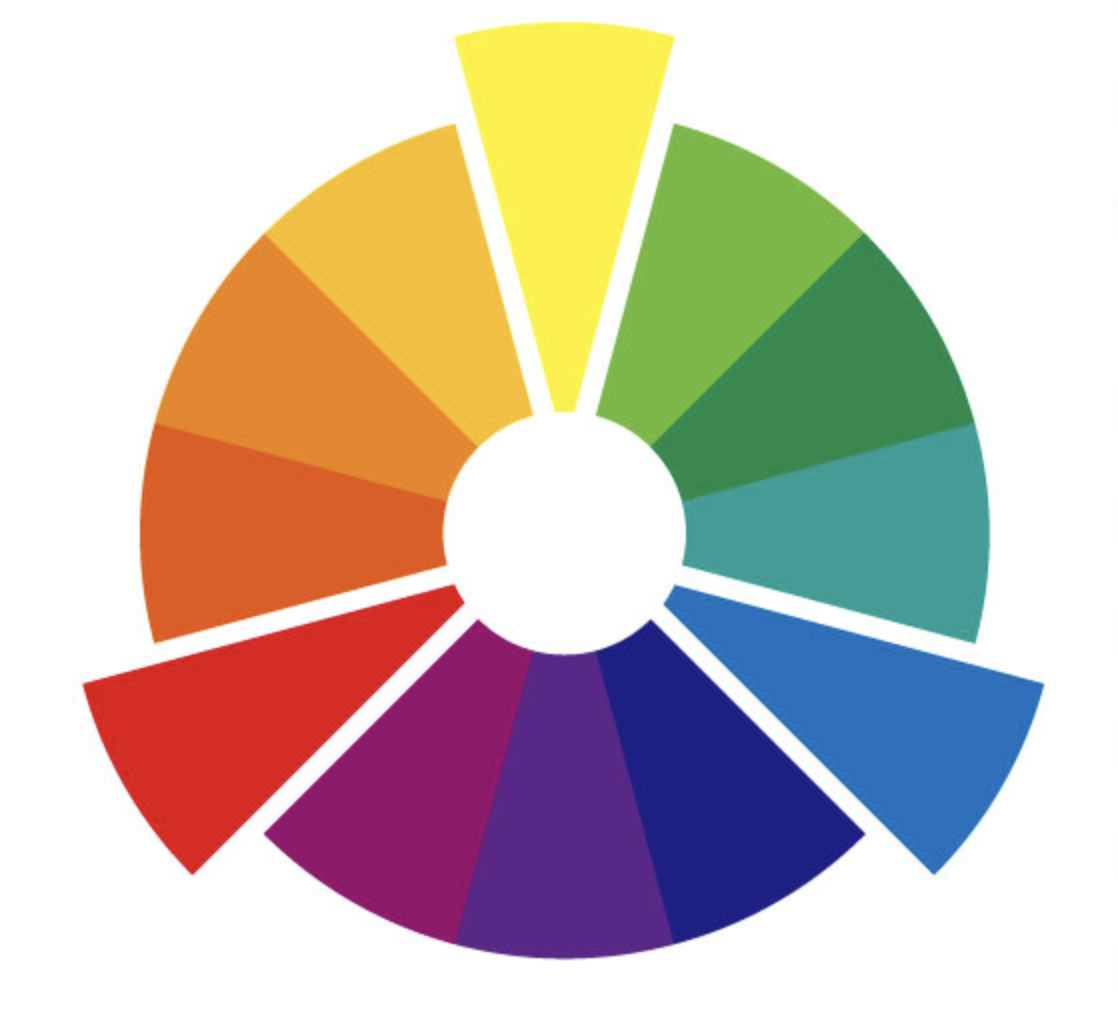

Color harmonies are created by using colors that are next to each other on the color wheel. They include complementary colors, analogous colors, and monochromatic colors.
Complementary colors are those that are opposite each other on the color wheel and create a strong contrast when used together.

Analogous colors are those that are next to each other on the color wheel and create a harmonious and balanced composition.

Monochromatic colors use different shades and tints of a single color.
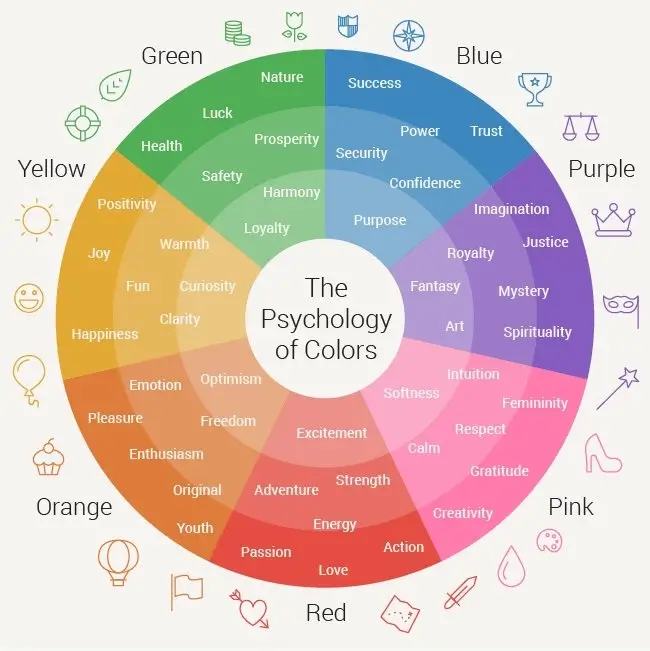
Color Psychology & Emotions
Color theory also includes the psychological and emotional effects of color. For example, warm colors like red and yellow can create feelings of warmth, energy and excitement, while cool colors like blue and green can create feelings of calm and serenity. Additionally, it's also important to note that color theory is not just about aesthetics but also the technical aspects of color like color management, color spaces, color models, and color reproduction.